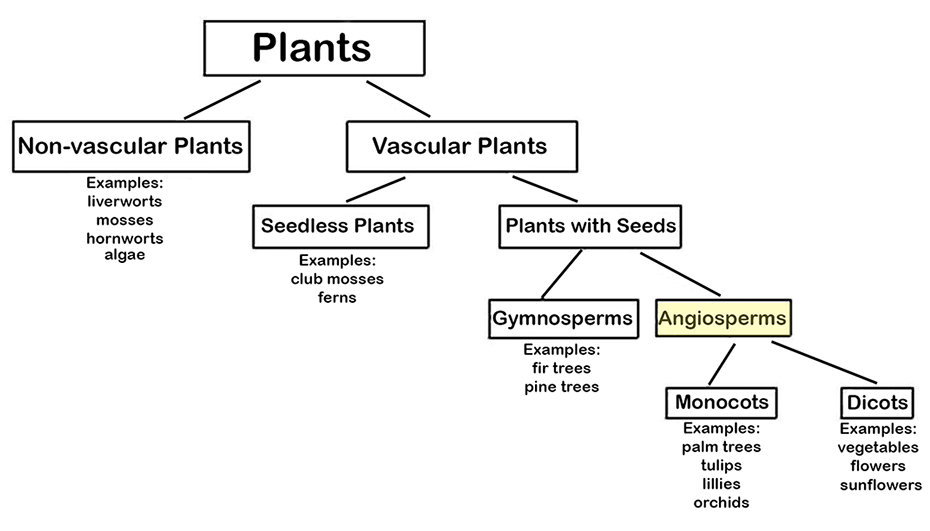
What are Angiosperms? Angiosperms are vascular plants with flowers that produce seeds. The seeds are inside a protective layer (such as a fruit). An interesting fact about angiosperms is that they did not exist until after mammals had evolved. So, earlier mammals did not get to enjoy flowers like we do!
Types of Angiosperms. As shown in the plant taxonomy tree below, there are two general types of Angiosperms: Monocots and Dicots:
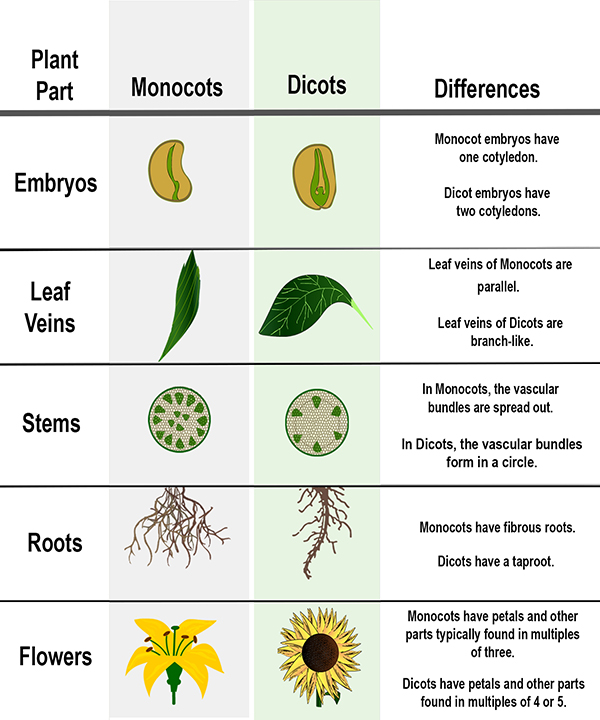
Monocots are angiosperms whose seeds have only one leaf inside of the shell, called a cotyledon (pronounced "Kaw-ta-LEE-don"). (“Mono” means “one” and “cot” is short for “cotyledon.”) This cotyledon leaf is like a “starter” leaf that provides nutrients to the growing plant until the “final” leaves grow and start making food. The cotyledon shrivels and dies once that happens. Examples of monocots are grasses, tulips and lilies. Monocots have petals in multiples of three (3, 6, 9, etc.) with long slender leaves. Monocots tend to have fibrous roots, but the roots are not deep.
Dicots are angiosperms with two seed leaves, or cotyledons. (“Di” means “two” and “cot” is short for “cotyledon.”) Some dicot angiosperms are roses, dandelions, sunflowers, and most of the flowers we see every day! Trees such as the maple and oak are dicots. Food plants like beans and apples are also dicots. These flowers have four or five petals (or multiples of four and five). Their leaves are usually wide with branching veins for carrying water. The picture below shows the development of a dicot (bean) plant from a seed to a young plant.
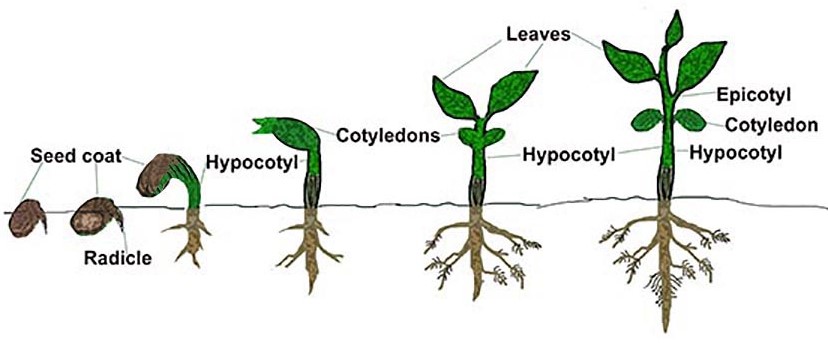
The picture above shows a “dicot” bean seed growing into a young bean plant. There are two “starter leaves,” or cotyledons, for bean plants. This is easiest to see in the two rightmost images.
The diagram below shows differences between monocots and dicots, including the embryos, vein pattern in the leaves, stems, roots and flowers.