

How quickly an object changes speed, or accelerates, in a given direction depends on the “net” force acting on the object in that direction.
Net force. The “net” force in a given direction is the sum of all forces acting in that direction minus the sum of all forces acting in the opposite direction.
In other words, equal forces on an object that are in opposite directions cancel each other out and do not affect the object's motion. Only the "left over" force in that direction will affect the object's acceleration in that direction. This "left over" force is the net force.
Then we find the total force acting on the body in the negative x-direction.
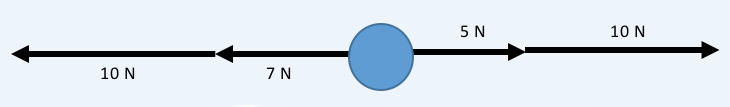
So, the net force on the body of the x-direction is: 15 N - 17 N = -2 N
The negative sign means that the net force on the body is 2 N in the negative x-direction (or to the left).
General definition of a "net" quantity. In general, the "net" of something is the total amount in one "direction" minus the total amount in the opposite "direction."
Other examples of "net" effects: