Two Types of Plants. Plants can be divided into Vascular and Non-Vascular Plants. This unit discusses non-vascular plants.
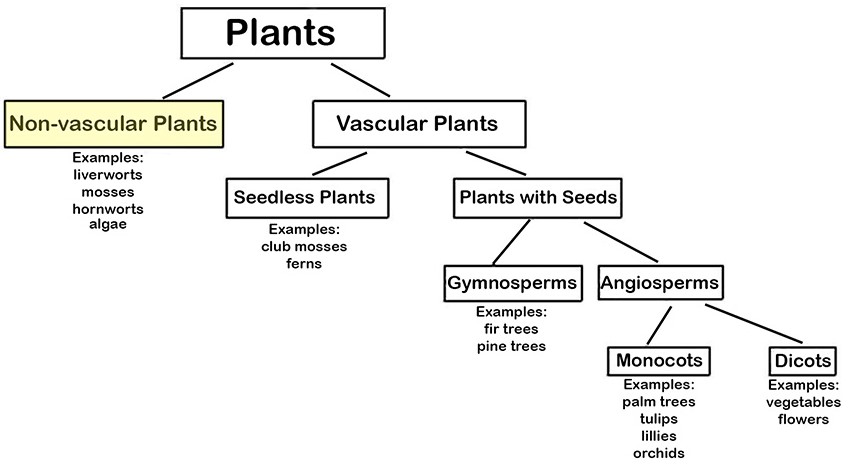
Non-vascular plants have very specific characteristics. The characteristics include lacking all of the following: (a) vascular tissue (cells that form tubes for transporting water and nutrients throughout the plant), (b) true leaves, (c) seeds, and (d) flowers. These plants do not have tubes to carry materials.
Materials including nutrients move slowly from one cell to another. Instead of roots, they have thin, hair-like structures (called rhizoids) that hold them to the ground. The rhizoids transfer water to the plants. For this reason, most of these plants are low to the ground and small, like mosses and green algae. Because they do not have true roots, non-vascular plants live in areas where there is a lot of water.
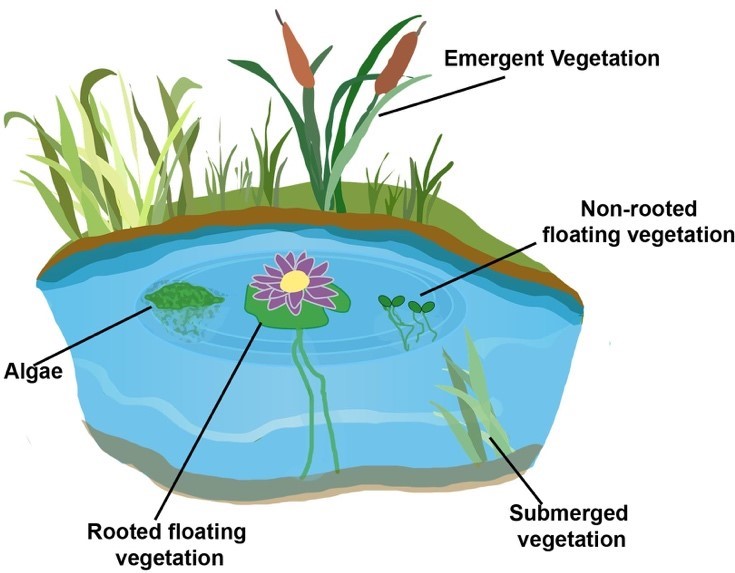
The picture below shows various forms of both vascular and non-vascular plants commonly found in ponds.