

The temperature of an object is defined as the average (translational) kinetic energy of its particles (molecules and atoms). The kinetic energy of each particle is related to both the mass of the particle and the speed of the particle.
Kinetic energy is defined as: KE (particle) = 1/2*m*v2
The temperature of an object is defined as the average of (1/2*m*v2) for all of the object's particles.
So, if something causes the particles of an object to start moving around faster, the temperature increases. But if something causes the particles of an object start to slow, the temperature decreases.
As shown below, when an object's particles move around faster, the object is at a higher temperature (Time 1). When they move around more slowly, the object is at a lower temperature (Time 2). (The particles stay the same size though.)
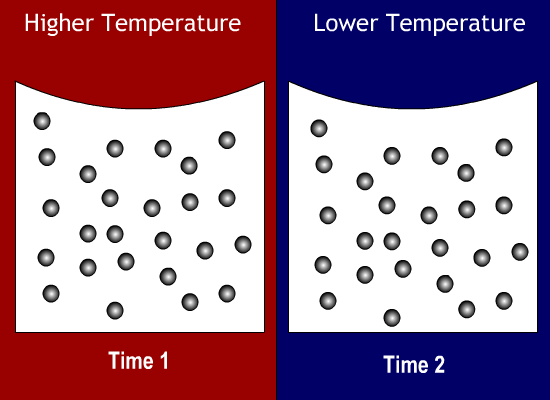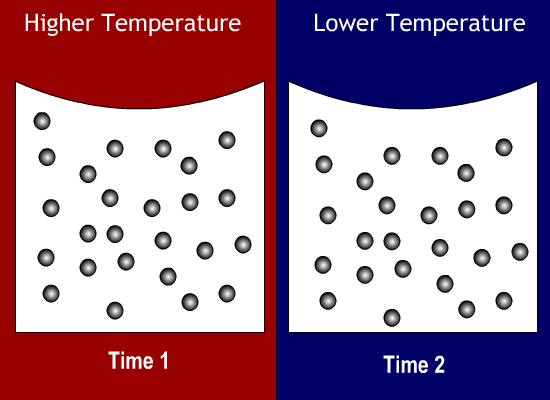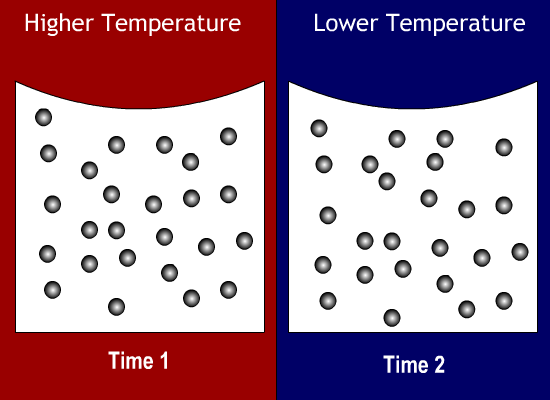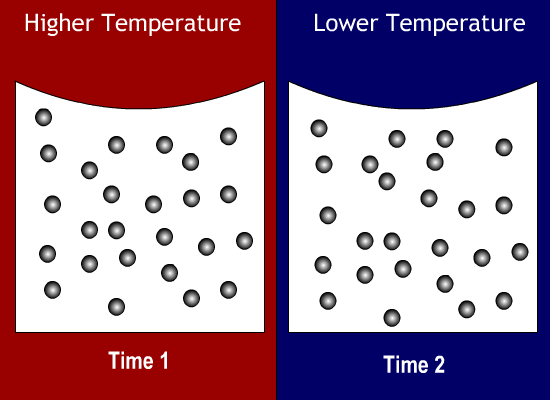
Temperature is measured in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit. In the United States, we mostly use Fahrenheit. But in science (and most of the rest of the world), the standard unit is Celsius.
In Fahrenheit, water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degress.
But in Celcius, water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees. (This is pretty easy to remember, right?)
The Fahrenheit and Celcius scales in the range of water freezing and boiling are shown on a number line below:
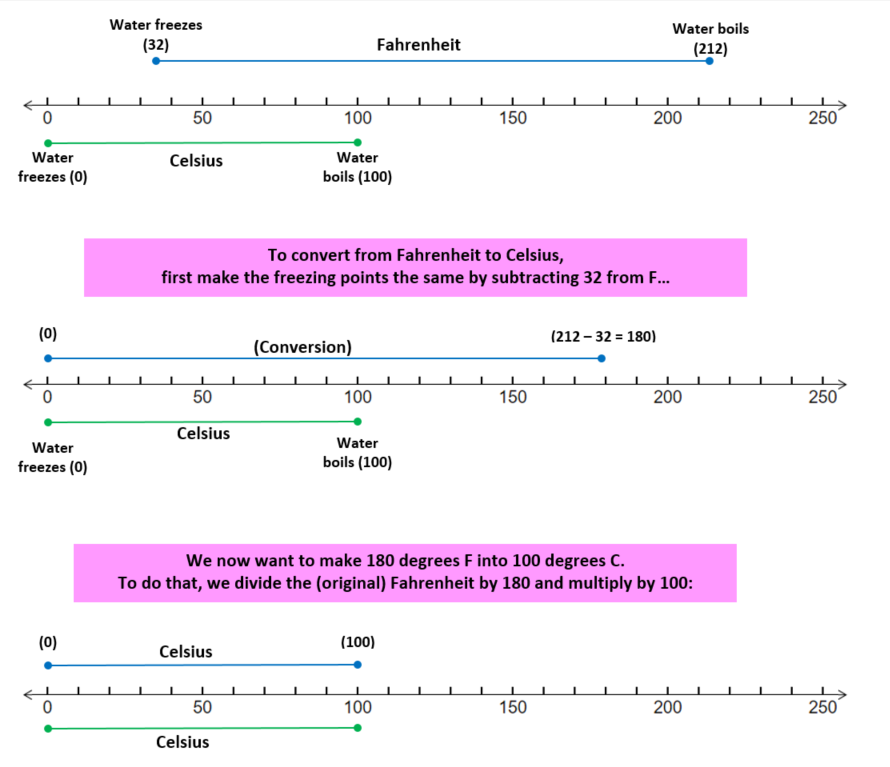
To summarize: degrees C = (°F - 32)*100/180
Simplifying the fraction: °C = (°F - 32)*5/9